Huntertown Roofing: What Are The 3 Primary Roof Designs?
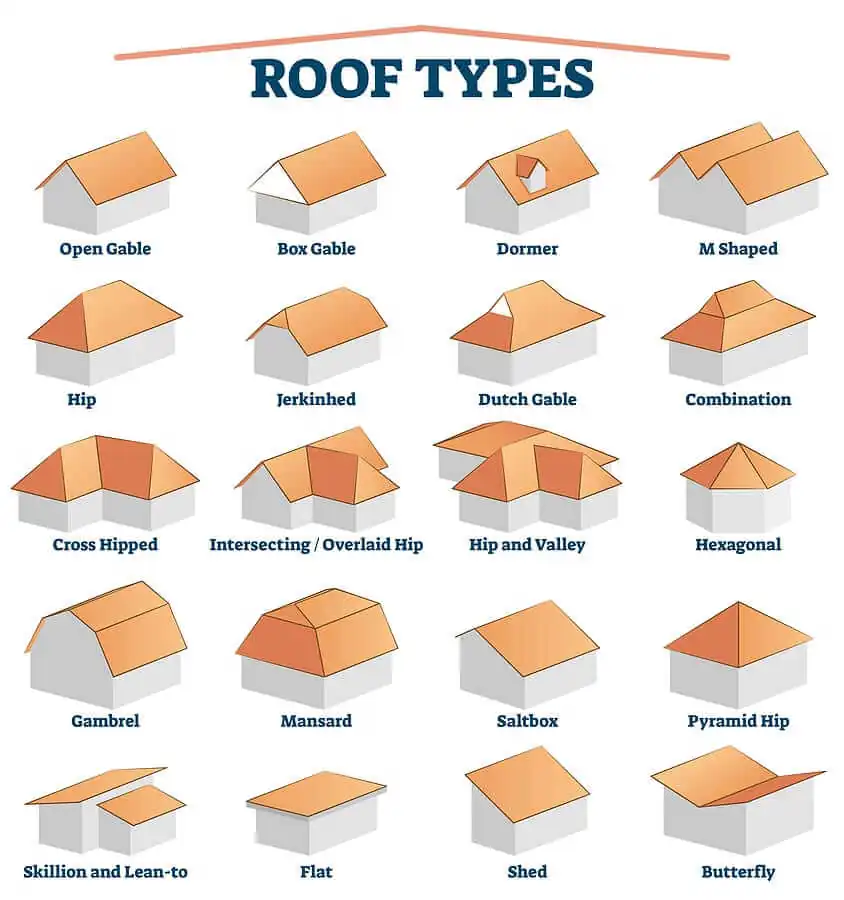
When it comes to Huntertown roofing, there are many designs, but three common roof types stand out due to their unique features and widespread use. Each design offers specific benefits, helping homeowners achieve their desired look, function, and durability. Here’s an overview of these primary roof designs to help you better understand your roofing options.
1. Hip Roof
A hip roof is characterized by its slopes on all four sides, which converge at the top to form a ridge. Unlike other roof types, it lacks vertical sides, making it highly recognizable. This design’s structure not only adds to its aesthetic appeal but also makes it exceptionally stable and robust. Variations of hip roofs include:
- Regular Hip: This simple version of a hip roof consists of four triangular faces, two of which are longer. It is commonly used for traditional homes, offering a symmetrical appearance and providing decent weather protection, although it tends to have limited attic space.
- Half-Hip: Combining elements of both gable and hip roofs, the half-hip version provides a unique aesthetic where the lower part of the roof resembles a gable, while the top ends in a hip. This style offers added structural strength and a distinctive look.
- Cross-Hip: Perfect for L-shaped buildings, this design combines two intersecting hip roof sections, creating a valley where they meet. Cross-hip roofs provide superior drainage and make an impressive visual statement.
Advantages of Hip Roofs:
- Superior Wind Resistance: Due to their aerodynamic design, hip roofs are ideal for regions prone to high winds and hurricanes, providing excellent stability.
- Efficient Drainage: The sloping design ensures effective water runoff, reducing the risk of leaks or water damage.
- Better Ventilation: Hip roofs can be combined with vents or dormers to enhance attic ventilation, keeping the interior cooler in the summer.
- Gutter Compatibility: They can accommodate wraparound gutters for seamless water management.
2. Gable Roof
The gable roof features two sloping sides that meet at a ridge, forming a triangular extension called a gable. This classic design remains a popular choice due to its practicality, simplicity, and timeless appeal. Variations of gable roofs include:
- Front Gable: The front gable style places the main entrance of the house beneath the gable, making a strong visual impact. It is commonly used in traditional and colonial-style homes.
- Side Gable: In this variation, the main entrance is located on the house’s side, away from the gable. This design often works well for homes with a rectangular layout.
- Cross Gable: Suitable for complex house layouts, cross gable roofs feature multiple gables that intersect at different angles, creating additional space and visual interest.
Advantages of Gable Roofs:
- Ease of Construction: Gable roofs are relatively simple to construct, making them a cost-effective option for many homeowners.
- Additional Space: The triangular shape creates additional attic space, which can be used for storage or even as living space.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to more complex roof styles, gable roofs are generally more affordable and use fewer materials.
- Efficient Water Runoff: The steep slopes allow for quick water drainage, reducing the risk of leaks and water accumulation.
3. Flat Roof
Flat roofs may appear nearly level, but they usually have a slight pitch to facilitate drainage. While they are often associated with commercial buildings, they have become increasingly popular for residential use, particularly for modern and contemporary home designs. Common flat roof types include:
- Membrane Roofing: Made from materials like rubber (EPDM), membrane roofing systems are lightweight and offer excellent waterproofing. They can be glued down or held in place with weights.
- Built-Up Roofing (BUR): This traditional flat roofing system consists of multiple layers of ply sheets, tar, and gravel, providing exceptional durability and resistance to the elements.
- Modified Bitumen: Comprising a mix of rubber and plastic materials, modified bitumen roofs are highly durable and ideal for areas with fluctuating temperatures.
Advantages of Flat Roofs:
- Cost-Effective Construction: Flat roofs are generally less expensive to install due to their simpler design and reduced need for materials.
- Extra Usable Space: They offer additional outdoor living space, which can be used for roof gardens, patios, or solar panel installations.
- Easy Maintenance and Inspection: The nearly level surface allows for quick and straightforward inspection, repairs, and maintenance tasks.
- Versatile Design: Flat roofs are highly adaptable, making them suitable for both traditional and contemporary building designs.
Choosing the Right Roof for Your Home
When selecting a roof design, it’s important to consider your home’s architectural style, local weather conditions, and your long-term needs. Hip roofs offer exceptional stability and resistance to harsh winds, while gable roofs provide a timeless, adaptable look with excellent drainage capabilities. Flat roofs, on the other hand, offer versatility and cost savings, making them ideal for certain applications.
The decision ultimately depends on your preferences and your home’s specific requirements. No matter which design you choose, working with a knowledgeable roofing professional can help ensure you make the best choice for your needs.






